Explore web search results related to this domain and discover relevant information.

Understand the law of supply in this educational video lesson. Learn about its principles in just 5 minutes and see why Study.com has thousands of 5-star reviews.
For instance, when Apple released the iPhone 5, they decreased supply in order to boost its demand. This prompted customers to queue up for days outside Apple stores. The high demand enabled Apple to set premium prices for the iPhone 5, which customers willingly paid. The law can lead to overstocking due to lower demand for a certain good.Similarly, during extreme weather conditions, essential products might sell out quickly, while during normal weather conditions, low demand may require stores to lower prices to clear supply. Read Law of Supply | Definition, Principle & Example LessonThe law of supply is a theory of how supply for certain goods and services influences their pricing. The higher the price of a good, the more willing are the manufacturers to increase their production.The aim of the law of supply is to balance inventory with consumer demand while also charging the maximum price they are willing to pay.
Discover how the law of supply impacts prices and quantities, and explore various types and examples that explain this fundamental economic principle.
The law of supply, a fundamental concept in microeconomics, asserts that as the price of a good or service rises, suppliers are eager to offer more of it, aiming to increase their profits. Conversely, if prices fall, suppliers typically provide less.Alfred Marshall, a British economist, significantly contributed to supply theory by using the supply curve to illustrate that both supply and demand set prices and output. The law of supply and demand collectively explains the balance in market economies, where sellers and buyers reach an equilibrium of price and quantity.The chart below depicts the law of supply using a supply curve, which is upward sloping. A, B, and C are points on the supply curve. Each point on the curve reflects a direct correlation between quantity supplied (Q) and price (P).In a competitive market, demand ultimately determines price, while the price sets the quantity suppliers are willing to supply. The law of supply, along with the law of demand, is essential in explaining how resources are allocated and prices are set in market economies.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/terms_l_lawofsupply_FINAL-63c8fbc006fb4bf4aeb50ea439991efa.jpg)

Learn how the law of supply and demand affects prices, whether supply remains the same and demand increases or vice-versa, plus the exceptions to the rule.
The law of supply and demand is an economic theory that explains how supply and demand are related to each other and how that relationship affects the price of goods and services. It's a fundamental economic principle that explains when supply exceeds demand for a good or service, prices fall.When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. The law of supply and demand describes the relationship between prices and quantities of goods in a market economy.When supply is greater than demand, prices drop; when demand is greater than supply, prices rise. Price elasticity of demand refers to the sensitivity of prices in relation to demand. A good has inelastic demand if consumption does not change much in response to a change in prices. The law of supply and demand applies to a nation's money supply, as well as to products and services.Increased prices typically result in lower demand, and demand increases generally lead to increased supply; however, the supply of different products responds to demand differently, with some products' demand being less sensitive to prices than others. Economists describe this sensitivity as price elasticity of demand; products with pricing sensitive to demand are said to be price elastic. Inelastic pricing indicates a weak price influence on demand. The law of demand still applies, but pricing is less forceful and therefore has a weaker impact on supply.
Explore the Law of Supply, a core economic principle explaining how price and other factors influence producer decisions and market quantity.
The Law of Supply is a fundamental economic principle explaining how producers react to changes in the market price of goods and services. It establishes a direct relationship between the price of a product and the quantity that sellers are willing and able to offer for sale.When prices increase, producers generally supply more of a product, and conversely, when prices decrease, they tend to supply less. This principle operates under the assumption that all other factors influencing supply remain constant, a concept economists refer to as “ceteris paribus.” · The core of the Law of Supply lies in the financial incentives driving producers.Conversely, expecting lower future prices may prompt producers to increase current supply before prices fall. The Law of Supply is visually represented by a supply curve, which illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity producers are willing to supply.Conversely, a decrease in price makes production less profitable, potentially leading to a “cost squeeze” where revenues might not adequately cover production expenses. In such scenarios, producers often reduce the quantity they supply to avoid losses or to allocate resources to more profitable ventures.
L&W Supply is your trusted construction materials and building supplies distribution partner with more than 275 branch locations across the USA.
From seamless ordering to on-time delivery, and everything in between, we go the extra mile to keep you on schedule. Our #1 focus is on getting you what you want, where you want it, when you want it.L&W Supply ServicesIsai Molina to lead the new branch serving Southern Oregon and Northern California BELOIT, WI — August 20, 2025 — L&W Supply, a nationwide distributor of interior building materials and construction supplies, is proud to announce the opening of its newest branch in Medford, Oregon, located at 2087 Lars Way.We stock the brands you trust. Our extensive inventory and nationwide distribution ensures you have the building supplies to complete your project on time and on budget.L&W Supply Products

Learn what the law of supply is, discover why it's important, review the formula for the law of supply and explore some practical examples of how it works.
The law of supply is a principle that relates the quantity of supply that companies offer to the price at which they sell each product. It helps businesses raise their revenue and meet market demands, which can help them increase their profits.Learning about the law of supply may help you predict your workplace's future revenue and find ways to boost profit.In this article, we discuss what the law of supply is, why it's important and the factors that can affect it, along with the law of supply formula and practical examples for you to review.Key takeaways:The law of supply is an economic principle that describes the relationship between the quantity of supply that a company has and the price of each product. It assumes an increase in a product's supply when the product's price increases. Typically, if prices increase, businesses increase their supply since they have the chance to earn a higher profit.If prices decrease, businesses may decrease their supply since they may receive a lower profit. The law of supply helps businesses measure their inventory needs, including the number of a product they may need to order.Related: What Is Supply Chain Management and Why Is It Important?
Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more.
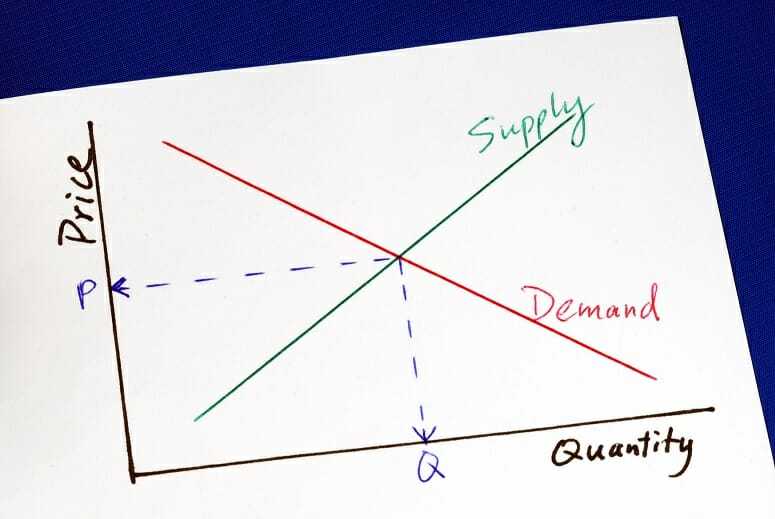
Price is a dominant factor in the determination of the supply of a commodity. As the price of a commodity increases, the supply of that commodity in the market also increases and vice-versa. This behaviour of the producers is studied through the law of supply.While price is a significant factor, other determinants such as production costs, technology, input prices, government policies, and expectations also impact supply. The Law of Supply, along with the Law of Demand, determines the market equilibrium price and quantity.While the Law of Supply generally holds true, there can be exceptions due to sudden technological advancements, natural disasters, changes in resource availability, or government interventions that disrupt market dynamics.In the above graph, the rising slope of the supply curve (SS) indicates a clear relationship between price and quantity supplied. The law of supply states the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied of a commodity after assuming that the other factors remain constant.
The latest developments in sustainable finance: US administration slams NBIM Caterpillar exit; ESG fund outflows 'could be due to shift from US managers'.
Home News & Analysis ESG round-up: Switzerland plans to adapt supply chain law to align with EU · Return to search · News & Analysis · The latest developments in sustainable finance: US administration slams NBIM Caterpillar exit; ESG fund outflows 'could be due to shift from US managers'.

The law of supply is a basic principle in economics that asserts that, assuming all else being constant, an increase in the price of goods
The law of supply is a basic principle in economics that asserts that, assuming all else being constant, an increase in the price of goods will result in a corresponding direct increase in the supply thereof.Taxes – The imposition of taxes in the production of goods limits profitability. If a producer is required to remit a portion of sales as tax, then the producer will be less inclined to increase supply. Legislation – Certain regulatory laws or quotas may be put in place that limit the quantity of a given product that can be produced.The law of supply depicts the producer’s behavior when the price of a good rises or falls. With a rise in price, the tendency is to increase supply because there is now more profit to be earned.The overarching relationship is between price and quantity, and applies only if all other factors remain constant. There are other factors that can affect the quantity supplied of a given.

The law of supply and demand is one of the simplest yet most powerful principles in economics. At its core, it explains how prices are set and why they
The law of supply and demand is one of the simplest yet most powerful principles in economics. At its core, it explains how prices are set and why they change. When demand for a product rises but supply stays the same, prices tend to go up. When supply increases but demand stays the same, prices usually drop.The law of supply and demand states that the price of a product is determined by the balance between how much people want it (demand) and how much of it is available (supply). When prices go up, suppliers are usually willing to produce and sell more, while buyers tend to purchase less.If the price goes above the equilibrium, supply will exceed demand, leaving unsold goods. If it falls below, demand will exceed supply, causing shortages. Markets naturally move toward this balance as buyers and sellers adjust their decisions in response to price changes. The law of supply and demand is easy to spot in everyday life.Similarly, new technology can make production cheaper, shifting the supply curve to the right. Movements are price-driven; shifts are caused by other factors that reshape the entire market. The law of supply and demand isn’t just about prices; it’s a lens for understanding how the world works.
We cannot provide a description for this page right now

Learn about the economic law of supply by understanding the definition, influential factors, various types, and two real-world examples of the idea in action.
In economics, several theories describe the order of business. One common concept is the law of supply. Learning about this rule can help you better understand the economic factors that influence a company's success.In this article, we discuss the definition of the rule of supply, uncover the factors that influence product availability, identify three supply types, and highlight several real-life examples of this economic principle in action.Key takeaways: The law of supply highlights a direct correlation between price and product availability, indicating that as a product or service's price increases, the quantity available also increases.There are three distinct types of supply: market supply (products or services offered by companies at a specific price during a set period), joint supply (products or services that yield two or more outputs, for example, cattle), and composite supply (a bundle of items sold together). ... The law of supply is an economic principle that states when all other factors are equal, as the price of a product or service increases, the quantity of that items also increases.It shows how suppliers maximize their profits by offering more products for sale as they increase the price. The law of supply also works in reverse, that as prices decrease, production and availability of the item also decreases.Because the company's objective is to make revenue and profit, as the market supports the demand of a product with a higher selling price, a company takes advantage of the opportunity by having more products or services for sale.

Discover how the law of supply and demand shapes prices, markets, and business strategy. Learn its definition, real-world examples, and why it matters.
Why did face masks suddenly become expensive in early 2020, then drop in price a year later ? Or why do the latest gaming consoles sell out instantly, only to appear on resale platforms at double the price? The answer lies in one of the most powerful concepts in economics: the law of supply and demand.Whether you’re a business owner setting product prices, an investor analyzing market opportunities, or a professional seeking to understand market dynamics, mastering supply and demand concepts provides the foundation for making informed, data-driven decisions that drive sustainable growth and competitive advantage. The law of supply and demand represents the fundamental economic principle that determines prices in a market economy.Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices typically fall. This continuous adjustment mechanism ensures efficient resource allocation across the economy. First articulated by Adam Smith in the 18th century and later refined by Alfred Marshall, the law of supply and demand has shaped economic thinking for over two centuries.This principle became central to modern market economics because it provides a framework for understanding price fluctuations, predicting market behavior, and making strategic business decisions. Today, businesses from retail giants to manufacturers use supply and demand analysis to optimize production schedules, pricing models, and market strategies. The law of supply establishes a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Following task force recommendations, ... passed laws that legalized homeowners’ ability to offer accessory dwelling units and duplexes in cities across the state, legalized multifamily construction in commercial zones and streamlined permitting. The policy success was dubbed the Montana Miracle, delivering hope for new housing supply in a state ...
Following task force recommendations, the 2023 Legislature passed laws that legalized homeowners’ ability to offer accessory dwelling units and duplexes in cities across the state, legalized multifamily construction in commercial zones and streamlined permitting. The policy success was dubbed the Montana Miracle, delivering hope for new housing supply in a state desperate for it.Instead, they saw that more remained to be done to legalize housing supply in Montana. They came back with a housing reform package just as impressive as the 2023 wins. Montana’s experience highlights some common themes as states look to limit localities’ restrictions on building housing: First, big changes often take more than one session to achieve. Second, one reform may reveal the need for additional reforms to make housing feasible to build. Third, pro-housing reforms may be subject to lawsuits, but statewide limits on local zoning authority are on strong legal ground.These developments don’t involve subdividing land into individual parcels for each home, but nonetheless have sometimes been required to go through the state’s notoriously onerous subdivision review. The law clarifies that this needn’t apply to manufactured housing parks, making it easier to add the least expensive type of new home to Montana’s housing supply.Two years ago, lawmakers in the Big Sky State passed one of the most comprehensive state-level housing reform packages in the country. This year, they doubled down on their success.


Navigating the Crossroads of Land, Law, and Minerals: The Resolution Copper Conundrum and U.S. Supply Chain Strategy
While Resolution Copper has proposed advanced water treatment systems and seepage collection, critics warn that groundwater depletion could harm local ecosystems and agricultural communities. Investors must weigh these risks against the project's potential to supply 25% of U.S.Copper, a cornerstone of decarbonization, is essential for grid modernization, EVs, and wind turbines. With global demand projected to surge by 400% by 2050, the U.S. faces a stark choice: either invest in domestic supply chains or cede influence to nations like China, which currently dominates 60% of global copper refining.However, the project's geopolitical value is contingent on its ability to navigate regulatory and cultural hurdles. Delays in permitting or production could disrupt supply chain timelines, creating volatility in copper markets.For investors, the path forward requires a nuanced understanding of public land policy, regulatory dynamics, and the geopolitical stakes of mineral security. While the project's potential to strengthen U.S. supply chains is undeniable, its long-term viability will depend on its ability to navigate a landscape where every permit, pipeline, and pipeline is a battleground.
Wholesale plumbing supply, located in South-West Arkansas, with over 11,000 line items in stock. Serving Magnolia since 1976, and now Nation Wide.

Companies will no longer be required to report on their efforts to reduce modern slavery as Berlin seeks to match EU efforts to reduce the compliance burden of sustainability rules.
How-to guide How-to guide: How to assess modern slavery risk in supply chains (USA) Recently updated
The law of supply is a fundamental principle of economic theory which states that, keeping other factors constant, an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied. In other words, there is a direct relationship between price and quantity: quantities respond in the same direction ...
The law of supply is a fundamental principle of economic theory which states that, keeping other factors constant, an increase in price results in an increase in quantity supplied. In other words, there is a direct relationship between price and quantity: quantities respond in the same direction as price changes.Some heterodox economists, such as Steve Keen and Dirk Ehnts, dispute the law of supply, arguing that the supply curve for mass-produced goods is often downward-sloping: as production increases, unit prices go down, and conversely, if demand is very low, unit prices go up.The law of supply and demand states that, for a given product, if the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied, then the price increases, which decreases the demand (law of demand) and increases the supply (law of supply)—and vice versa—until the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.In short, the law of supply is a positive relationship between quantity supplied and price, and is the reason for the upward slope of the supply curve.A supply is a good or service that producers are willing to provide. The law of supply determines the quantity of supply at a given price.
In response to the recent Roseland plant explosion, Mike Brandner Law is helping residents and businesses recover damages for personal property and business losses, displacement costs, and insurance disputes. This week, the firm filed a class action lawsuit to hold Smitty’s Supply accountable.
ROSELAND, LA, United States, September 4, 2025 -- Mike Brandner Law is offering legal support to residents and businesses impacted by the recent explosion at the Smitty’s Supply plant in Roseland, Louisiana. The incident has left many in Tangipahoa and St.“Just this week we filed a class action lawsuit against Smitty’s Supply seeking damages for property damage, environmental cleanup, health-related injuries, inconvenience, and pain and suffering,” shared attorney Mike Brandner.While the cause of the explosion remains under investigation, records from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) show Smitty’s Supply has a history of violations, with prior pollutant levels far exceeding federal standards.Stock Quote API & Stock News API supplied by www.cloudquote.io Quotes delayed at least 20 minutes.

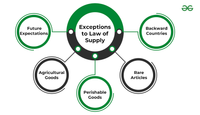
How to use the law of supply to make supply and pricing decisions, plus other factors to consider and exceptions when the law doesn't apply.
The law of supply is an economic theory that predicts how the price of goods and services affects their supply. It says that as prices rise, businesses will increase the amount of goods and services that they make available.Still, understanding the law of supply, as well the exceptions to the law and other relevant factors, can help companies determine how to price their products and services and adjust their supply to maximize profits.The law of supply is a basic economic concept. It states that an increase in the price of goods or services results in an increase in their supply. Supply is defined as the quantity of goods or services that suppliers are willing and able to provide to customers.The law works like this: Rising prices mean that products become more profitable, assuming other factors such as production costs remain constant. The prospect of higher profits therefore motivates businesses to supply more of these products. Existing suppliers may increase the supply of more profitable products at the expense of less profitable ones.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/terms_l_lawofsupply_FINAL-63c8fbc006fb4bf4aeb50ea439991efa.jpg)




